learnpython24-(Python if...else Statement)
Python if...else Statement
In this article, you will learn to create decisions in a Python program using different forms of if..else statement.
What is if...else statement in Python?
Decision making is required when we want to execute a code only if a certain condition is satisfied.
The if…elif…else statement is used in Python for decision making.
Python if Statement Syntax
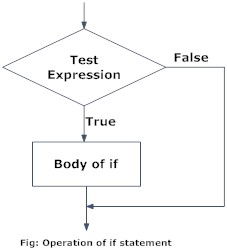
if test expression:
statement(s)Here, the program evaluates the test expression and will execute statement(s) only if the test expression is True.
If the test expression is False, the statement(s) is not executed.
In Python, the body of the if statement is indicated by the indentation. The body starts with an indentation and the first unindented line marks the end.
Python interprets non-zero values as True. None and 0 are interpreted as False.
Python if Statement Flowchart
Example: Python if Statement
# If the number is positive, we print an appropriate message
num = 3
if num > 0:
print(num, "is a positive number.")
print("This is always printed.")
num = -1
if num > 0:
print(num, "is a positive number.")
print("This is also always printed.")3 is a positive number This is always printed This is also always printed.
In the above example, num > 0 is the test expression.
The body of if is executed only if this evaluates to True.
When the variable num is equal to 3, test expression is true and statements inside the body of if are executed.
If the variable num is equal to -1, test expression is false and statements inside the body of if are skipped.
The print() statement falls outside of the if block (unindented). Hence, it is executed regardless of the test expression.
Python if...else Statement
Syntax of if...else
if test expression:
Body of if
else:
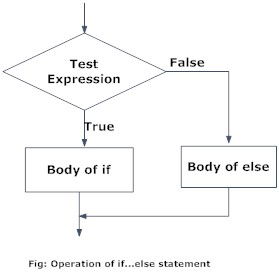
Body of elseThe if..else statement evaluates test expression and will execute the body of if only when the test condition is True.
If the condition is False, the body of else is executed. Indentation is used to separate the blocks.
Python if..else Flowchart
Example of if...else
# Program checks if the number is positive or negative
# And displays an appropriate message
num = 3
# Try these two variations as well.
# num = -5
# num = 0
if num >= 0:
print("Positive or Zero")
else:
print("Negative number")Positive or Zero
In the above example, when num is equal to 3, the test expression is true and the body of if is executed and the body of else is skipped.
If num is equal to -5, the test expression is false and the body of else is executed and the body of if is skipped.
If num is equal to 0, the test expression is true and body of if is executed and body of else is skipped.
Python if...elif...else Statement
Syntax of if...elif...else
if test expression:
Body of if
elif test expression:
Body of elif
else:
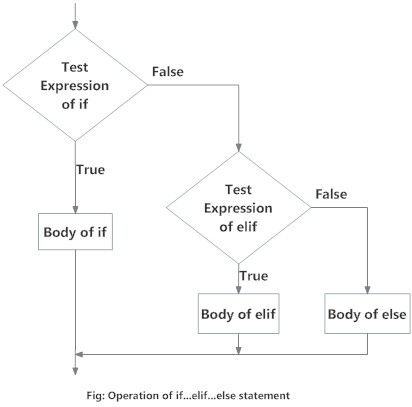
Body of elseThe elif is short for else if. It allows us to check for multiple expressions.
If the condition for if is False, it checks the condition of the next elif block and so on.
If all the conditions are False, the body of else is executed.
Only one block among the several if...elif...else blocks is executed according to the condition.
The if block can have only one else block. But it can have multiple elif blocks.
Flowchart of if...elif...else
Example of if...elif...else
'''In this program,
we check if the number is positive or
negative or zero and
display an appropriate message'''
num = 3.4
# Try these two variations as well:
# num = 0
# num = -4.5
if num > 0:
print("Positive number")
elif num == 0:
print("Zero")
else:
print("Negative number")When variable num is positive, Positive number is printed.
If num is equal to 0, Zero is printed.
If num is negative, Negative number is printed.
Python Nested if statements
We can have a if...elif...else statement inside another if...elif...else statement. This is called nesting in computer programming.
Any number of these statements can be nested inside one another. Indentation is the only way to figure out the level of nesting. They can get confusing, so they must be avoided unless necessary.
Python Nested if Example
'''In this program, we input a number
check if the number is positive or
negative or zero and display
an appropriate message
This time we use nested if statement'''
num = float(input("Enter a number: "))
if num >= 0:
if num == 0:
print("Zero")
else:
print("Positive number")
else:
print("Negative number")Enter a number: 5 Positive number
Enter a number: -1 Negative number
Output 3
Enter a number: 0 Zero
Comments
Post a Comment